The first 8 winning projects of the Strategic Innovation Open Call are officially kicking off! CARGOBIKE-SCALE, DAVER, HYBUHTRAIN, MUDAV, PantoTech, PGfor_Resilient_Cities, TRACE and TWINOPT cover five sectors being urban logistics, public transport, mobility data management, mobility and health, and electrification of transport and alternative fuels. The projects will see collaboration from 41 partners from across 16 countries.
In 2025 EIT Urban Mobility launched the new Strategic Innovation Open Call. The Call invites innovators from across Europe to submit proposals aimed at accelerating the deployment of impactful solutions to address the most pressing challenges in urban mobility. 58 applications were received for the Call’s first cut-off date in September 2025. These eight projects will in total receive 9 million euros in EIT Urban Mobility funding.
The Call focuses on supporting ambitious, market-critical projects that tackle clearly defined problems faced by cities, public authorities, and mobility providers. Through this Call, EIT Urban Mobility aims to strengthen Europe’s competitiveness by fostering collaboration across education, research, business and cities, as well as to enable large-scale deployment by backing solutions with a clear path to market and the potential to scale across Europe. “By supporting these innovative projects, we are accelerating the deployment of solutions to address pressing urban mobility challenges, while reinforcing Europe’s strategic capacity to scale innovation” said Adriana Diaz, Director of Innovation at EIT Urban Mobility. “In doing so, we are helping to build a strong ecosystem that delivers measurable, lasting benefits for citizens and communities”.
The next proposal cut-off date for the Strategic Innovation Open Call is 18 June 2026. For more information visit the call webpage.
The first projects of the Strategic Innovation Open Call are:
CARGOBIKE-SCALE – AI infrastructure for scaling cargo bike logistics across Europe
The CARGOBIKE-SCALE project addresses the rapid growth of urban freight and its impacts on climate and liveability. Motorised freight generates a large share of urban emissions and contributes to traffic congestion. Concurrently, parcel volumes are accelerating. This makes traditional van-based logistics fundamentally unsustainable, especially as cities expand zero-emission zones and tighten freight regulations.
Light electric vehicles (LEVs), such as cargo bikes, have on average around 95% lower CO2 emissions compared with vans and outperform motorised vehicles in dense urban areas. Additionally, the ability of cargo bikes to park closer to final delivery points and travel faster in congested conditions can reduce delivery time by 60%. However, most logistics operators, particularly SMEs, struggle to scale beyond pilots due to operational complexity. Successful deployments depend on sophisticated coordination, planning, and data-driven decision-making that is currently accessible only to larger organisations.
CARGOBIKE-SCALE will focus on building the missing digital coordination infrastructure required for systematic LEV deployment and scaling. The project will deliver a suite of interoperable digital platforms serving different market needs including coordination of vehicle types across networks enabling advanced logistics models to scale, business intelligence and strategic planning tools for SMEs, simulation technology for operators transitioning to mixed fleets. Pilots in Brussels (Belgium), Paris (France), London (UK), and Barcelona (Spain) will demonstrate technical readiness, regulatory adaptability, and pan-European replicability.
By enabling systematic LEV adoption, the project is expected to unlock 500,000–1 million tonnes of direct CO₂ savings annually by 2030, alongside major reductions in congestion, and air and noise pollution. Economically, it democratises advanced logistics technology, allowing SMEs to compete with large corporations and enabling local businesses to offer affordable, sustainable delivery.
Partners: Kale AI (lead partner) (UK), IT University of Copenhagen (DK), Cargonautes (FR), BIKELOGIC (ES), urbike (BE), University of Westminster (UK)
Total budget: 1,7M euros
Project duration: 2 years

DAVER – Data for vehicle emissions and noise remote sensing
It is estimated that between 3%-5% of high emitting vehicles are responsible for between 19% to 60% of the total on-road traffic emissions, the main source of emissions directly affecting human health and contributing to climate change. However existing enforcement policies often rely on blanket restrictions that are costly and not aligned with real-world vehicle performance. DAVER offers a targeted, data-driven alternative. The project will develop, validate and deploy an enforcement-ready system for the continuous, real-world monitoring of vehicle emissions and noise in urban environments.
At the core of DAVER is a new generation of autonomous remote sensing devices capable of operating 24/7 to measure true vehicle emissions and noise under real driving conditions. The sensing hardware is coupled with a secure digital platform that enables real-time alerts, high-emitter identification, enforcement workflows, data sharing and policy evaluation. Together, they form a scalable solution compatible with the European Commission’s 2025 Roadworthiness Package.
DAVER will be piloted in Barcelona (Spain), Thessaloniki (Greece) and Groningen (Netherlands) during which the system will analyse at least 100,000 vehicles and generate more than 40,000 records correlating noise levels with pollutant emissions. This data will validate the performance of the solution, demonstrate its applicability for low emission zone (LEZ) enforcement, and provide city authorities with insight into real-world vehicle behaviour.
DAVER allows authorities to take selective action against gross emitters to improve air quality and reduce urban noise. This targeted approach supports fairer mobility policies, increases public acceptance of clean transport measures, strengthens compliance with EU law and supports cities in meeting upcoming EU regulatory obligations.
Partners: Major Development Agency Thessaloniki (GR), Barcelona City Council (ES), Centre For Research & Technology Hellas (GR), FACTUAL (lead partner) (ES), Opus Remote Sensing (ES), Vinces Consulting (ES), Homan-Brinkman BV (NL)
Total budget: 1,52M euros
Project duration: 1.5 years

HYBUHTRAIN – Hydrogen engine and battery plug-in hybrid train
The HYBUHTRAIN project aims to deliver and demonstrate the world’s first hydrogen engine–battery plug-in hybrid train retrofit kit for passenger diesel multiple units (DMUs). Its core objective is to enable the rapid, cost-effective conversion of existing diesel trains into clean, efficient, zero-emission capable vehicles, helping European rail operators meet decarbonisation targets without waiting for slow and costly fleet replacement. The project will conduct a full operational demonstration of a retrofitted train in Poland.
On average 57% of European railway lines are electrified. However, thousands of DMUs operate on non-electrified lines, particularly in regional and suburban corridors, emitting CO₂, NOx, and particulate matter. With many DMUs having 10–20 years of remaining service life, full replacement with new zero-emission rolling stock is slow and costly, making retrofitting a more viable pathway to meet climate goals within relevant timelines.
HYBUHTRAIN builds directly on the EIT Urban Mobility co-funded HYIPTRAIN project, which demonstrated a hydrogen internal combustion engine (H₂-ICE) train. The HYBUHTRAIN project adds a railway-certified battery system, electric motor, and advanced energy management system, creating a hybrid configuration that reduces hydrogen consumption by 20–35%, increases operational range, enables regenerative braking, and allows zero-emission entry and acceleration in stations and urban areas.
The retrofit kit solution is platform-agnostic and designed for replication across diverse DMU fleets, regardless of age or manufacturer. Installation is depot-based rather than OEM-dependent, enabling rapid, parallel deployment across regions. The modular architecture supports multiple configurations, including hydrogen-battery hybrids, battery-diesel hybrids, and full battery-electric conversions, allowing operators to choose solutions aligned with their duty cycles and infrastructure.
Partners: Riga Technical University (LV), DIGAS (lead partner) (LV), Mikroluch (UA), SKPL, Municipality of the City of Rzeszów (PL)
Total budget: 1,16M euros
Project duration: 2 years

MUDAV – Multi-purpose urban delivery with autonomous vehicle
E-commerce revenue in Germany increased in 2024 rising to over 88 billion euro and the fast-moving consumer goods delivery sector experienced almost double the growth rate compared to other sectors. This continuing growth of e-commerce is placing urban logistics under growing pressure – intensifying congestion, emissions, competition for curb space, and putting operational strain on logistics providers. At the same time, companies face driver shortages, ambitious decarbonisation targets, and rising expectations for fast, reliable service. Existing pilot solutions, such as small delivery robots or limited autonomous vehicle trials, have demonstrated technical feasibility but have not yet achieved full process integration or commercial scalability. The MUDAV project addresses this by transitioning to a fully integrated, scalable, and commercially viable logistics model.
Building on successful deployments by LOXO with Planzer (parcel delivery in Bern) and REWE (online grocery delivery), MUDAV consolidates these learnings into a next-generation autonomous vehicle platform. Based on a European 3.5-ton electric light commercial vehicle, the LOXO Delta offers a six-pallet capacity and is designed to serve multiple use cases such as dynamic microhubs and last-mile grocery delivery.
The project’s objective is to deploy the first fully integrated Level 4 autonomous delivery fleets in Zurich (Switzerland) and Bochum (Germany). Together MUDAV project partners will define vehicle and operational requirements, validate a projected 30% cost reduction, and assess impacts on daily kilometres travelled and CO₂ emissions. Technologically, the project overcomes traditional barriers to autonomous deployment through virtual mapping and advanced simulation. Scalable virtual mapping, combining satellite imagery, street-level data, and vehicle inputs enables faster, safer, and more economical rollouts in complex urban settings.
Partners: Planzer Transport (CH), Bochum Economic Development (GE), LOXO (lead partner) (CH), Rewe digital (GE), Canton of Zurich – Office of Mobility and Transport (CH)
Total budget: 2,6M euros
Project duration: 2 years

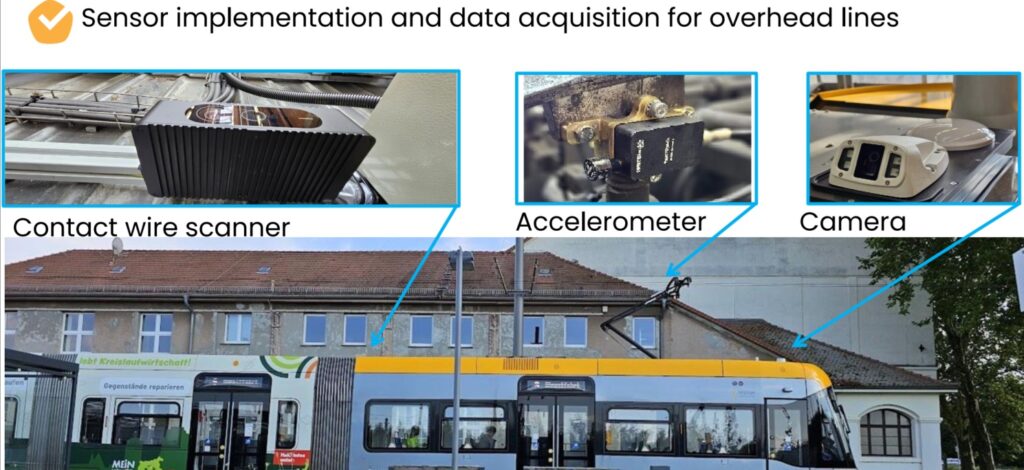
PantoTech – safe, resilient mobility systems through intelligent tram and metro catenary monitoring
Europe has a well-established electric light rail network accounting for 58% of the kilometre global total and generating 75% of the total ridership. However these systems face the persistent challenge of maintaining overhead contact systems (OCS) efficiently, safely, and cost-effectively. Traditional maintenance practices rely heavily on time-based inspections, manual measurements, and reactive interventions. These approaches consume significant crew hours, expose workers to hazardous conditions, and often fail to detect hidden or emerging faults before they escalate into costly and dangerous incidents. As infrastructure ages and skilled personnel become scarcer, this model is increasingly unsustainable.
PantoTech addresses this challenge by introducing an AI-driven, predictive maintenance platform tailored to urban rail electrification. The project will integrate advanced vibration analysis with real-time monitoring of the three safety-critical OCS parameters required by light rail operators: height, zigzag, and wire thickness. By transforming raw operational data into actionable insights, PantoTech enables infrastructure managers to detect high-risk faults early, prioritise interventions, and shift decisively from reactive to proactive asset management.
The solution’s predictive monitoring reduces manual inspections, prevents service delays, and improves working conditions for maintenance crews. In the long term, cities will benefit from safer and more resilient public transport networks, extended infrastructure lifecycles, and lower operational costs. Beyond operational benefits, PantoTech supports more reliable tram and metro services, encouraging modal shift away from private cars, reducing congestion and emissions.
The project will validate and advance the platform through pilot deployments in Prague (Czechia), Debrecen (Hungary), Istanbul and Konya (Türkiye).
Partners: Technical University of Berlin (lead partner) (GE), PANTOhealth GmbH (GE), City of Istanbul: Metro Istanbul (TR), Konya Metropolitan Municipality (TR), DKV Debrecen Public Transport Company (HU), Czech Technical University in Prague (CZ)
Total budget: 2,25M euros
Project duration: 2 years
PGfor_Resilient_Cities – the dynamic optimisation of construction logistics for resilient and liveable cities
The PGfor_Resilient_Cities project addresses the pressing yet often overlooked urban mobility challenge related to the inefficiency of construction logistics, with a specific focus on concrete. The most widely used construction material in cities, in Europe the read-mix concrete market is forecast to reach 65 billion euro by 2031. Yet today, concrete deliveries in urban areas are often managed through fragmented, largely manual processes that lead to unnecessary vehicle movements, empty trips, delays, and downtime. These inefficiencies translate directly into traffic congestion, noise, air pollution, higher CO₂ emissions, and rising operational costs for companies.
The project will develop and pilot an intelligent, cloud-based platform that dynamically optimises concrete deliveries in real-time. Using advanced algorithms, the system automatically coordinates transport operations, adapting to changing conditions such as delays, site readiness, traffic, or production constraints. Unlike traditional logistics or ERP systems, which are often too complex and costly for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), this solution is designed as a specialised, autonomous optimisation module. It allows construction companies and concrete suppliers to benefit from advanced logistics optimisation without the burden of heavy IT infrastructure or manual planning.
By optimising routing and scheduling, companies can expect lower fuel consumption CO₂ emissions by an estimated 8–12% for vehicles managed by the PGfor_Resilient_Cities solution. The platform will generate high-quality operational and environmental data, enabling companies to meet growing demands for emissions reporting and sustainability accountability.
The PGfor_Resilient_Cities builds on the previously EIT Urban Mobility co-funded foundational platform into a fully intelligent, autonomous ecosystem that will be demonstrated in Poland and Ukraine to validate both scalability and resilience.
Partners: ProperGate (lead partner) (PL), Astor Invest (UA), Bosta-Beton (PL)
Total budget: 1,09M euros
Project duration: 1 year

TRACE – tram assistance for safe and efficient mobility
Public transport (PT), especially trams, plays a key role in the European Green Deal objective of reducing transport-related greenhouse gas emissions by 90%. Trams emit nine times less CO₂ and consume six times less energy than cars, but their full potential depends on improving safety, efficiency and reliability. The TRACE project aims to significantly enhance the safety, efficiency, and reliability of urban tram systems through an Advanced Driver Assistance System (ADAS) tailored specifically to light rail vehicles. Building on the EIT Urban Mobility co-funded ARISE project, TRACE responds directly to growing safety challenges, operational inefficiencies, and staff shortages faced by public transport operators (PTOs) as cities become denser and more multimodal.
Trams are a cornerstone of sustainable urban mobility, emitting less CO₂ and consuming less energy than private cars. However, their full potential is constrained by safety risks with trams sharing space with cars, pedestrians, cyclists, and micro-mobility users, yet are unable to swerve to avoid obstacles.
TRACE addresses these challenges by validating the upgraded capabilities of the OTIV.TWO ADAS, including side collision avoidance, predictive collision detection, enhanced digital mapping and overspeed protection. Together, these features provide tram drivers with real-time situational awareness and proactive decision support. These will enable earlier hazard detection, smoother driving, and reduced service disruptions.
The project will conduct pilots in Ghent (Belgium), Karlsruhe (Germany), and Rotterdam (Netherlands). The pilot will involve 16 trams and more than 400,000 km of operational data. From testing, the project will refine predictive algorithms, ensure compliance with rail standards, and demonstrate measurable performance improvements in relation to obstacle detection accuracy, journey time and collisions.
Partners: Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya – CARNET (lead partner) (ES), OTIV BV (BE), De Lijn (BE), Albtal Transport Company Ltd (GE)
Total budget: 3,6M euros
Project duration: 2 years

TWINOPT – real-time digital twins for forecasting and optimising urban transport operations
The TWINOPT project will deliver a real-time, operational digital twin for traffic management, enabling cities to move from static planning tools to live, data-driven decision-making. TWINOPT advances validated digital twin concepts into a procurement-ready, scalable solution that supports day-to-day traffic operations.
Urban traffic control rooms still rely on siloed data and tools that are too slow and outdated for real-time use. Thus cities often struggle to anticipate congestion, respond effectively to incidents, prioritise public transport, and reduce emissions. TWINOPT will deliver a vendor-agnostic platform for traffic control rooms. The platform will integrate multiple live data feeds, generates short-term forecasts, detects anomalies, and enables rapid ‘what-if’ analyses using a simulation engine.
The solution will be piloted in Jesi (Italy), Cambridgeshire (UK), and Antalya (Türkiye), with each pilot integrating at least two live data feeds, delivering forecasts with low error rates and minimal latency.
TWINOPT will enable faster and better-justified responses to incidents, improved transport reliability, reduced congestion, and measurable reductions in delays and CO₂ emissions.
Partners: Transcality (CH), Antalya Metropolitan Municipality (TR), Piemonte Innova Foundation (lead partner) (IT), Greater Cambridge Partnership (UK), Municipality of Jesi (IT)
Total budget: 717K euros
Project duration: 2 years
For more information on the Strategic Innovation Open Call and its next cut-off date visit the call webpage.




